Introductie: Padel en tennis verschillen sterk in speelveld, regels, materiaal en vereiste vaardigheden. Padel gebruikt glazen wanden als onderdeel van het spel en vereist snelle reflexen met strategische balcontrole, terwijl tennis draait om kracht, snelheid en een grotere baan. In dit artikel lees je alles over de verschillen in courts, racket- en baltype, spelregels en benodigde skills. Ontdek welke sport jouw speelstijl het beste aanvult met gedetailleerde info per onderdeel.

What are the differences in court size between padel and tennis?
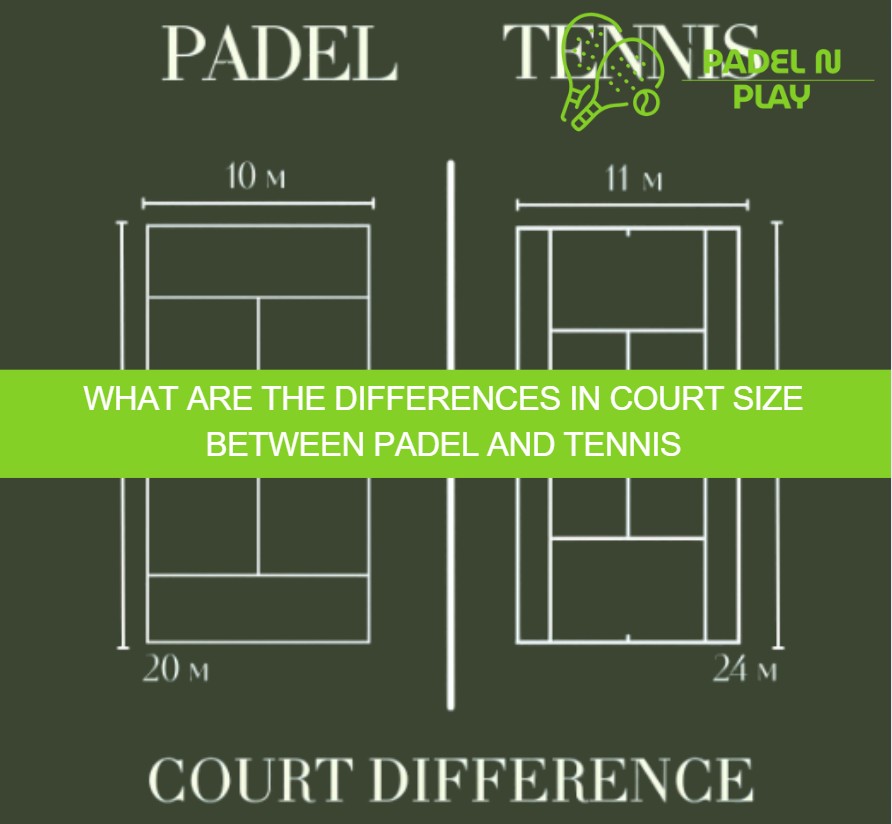
The main differences in court size between padel and tennis relate to dimensions, boundaries, and player capacity.
- Padel courts measure 10 meters wide by 20 meters long, totaling 200 m², and are enclosed by walls of glass or metal mesh. The enclosure enables rebound play, which adds tactical depth and prolongs rallies.
- Tennis courts for singles measure 8.23 meters wide by 23.77 meters long (≈195.7 m²) and for doubles 10.97 meters wide (≈260.9 m²). They are open courts, where the lines define the boundaries and no structural enclosures influence the gameplay.
What are the main features of a padel court?
The features of a padel court include:
- Enclosed glass and metal mesh walls
- Dimensions: 10 m x 20 m
- Net height: 88 cm in the center, 92 cm at the posts
- Playing surface: artificial grass, often with sand infill
- Metallic or glass back walls, 3 meters tall at the back and up to 4 meters on the sides
What are the main features of a tennis court?
The features of a tennis court include:
- No external walls; boundaries are defined by lines
- Dimensions: 23.77 m x 8.23 m (singles) or 10.97 m (doubles)
- Net height: 91.4 cm at center
- Surface types: hard court, clay, or natural grass
- Surface properties affect speed, bounce, and player movement
How does serving differ in padel versus tennis?
The primary difference in serving between padel and tennis lies in technique and allowable height.
- Padel requires an underhand serve where the ball must be hit below waist level after bouncing once on the ground. The serve must land in the opposite service box.
- Tennis allows an overhand serve without a bounce. Tennis players often use spin and power to gain an advantage with the first stroke.

What are the serve rules specific to padel?
Padel serve rules require:
- Serving underhand after a bounce
- Ball contact below waist level
- Serve directed diagonally into the opponent’s service box
- Serve must not touch the wire mesh after bouncing in the service box
What are the serve rules specific to tennis?
Tennis serve rules include:
- Two serve attempts per point
- Serve must land in the diagonal service box
- Overhand motion allowed from behind the baseline
- Sand, clay, or grass surface may influence serve effectiveness
What are the differences in balls used for padel and tennis?
The balls used in padel and tennis differ in internal pressure and speed.
- Padel balls have a lower pressure of 10–11 psi, producing less bounce and speed, making them more controllable and suitable for wall rebounds.
- Tennis balls use 14 psi pressure, resulting in higher bounce, faster trajectory, and greater surface wear. These properties match the longer distances and open play of tennis courts.
How does ball pressure affect gameplay?
- Lower-pressure balls (padel) reduce rally velocity and encourage longer exchanges
- Higher-pressure balls (tennis) generate faster ball speeds and less dwell time per stroke
- Consistency of bounce is more variable in tennis due to diverse court surfaces
Are padel balls similar to tennis balls in appearance?
Yes, padel balls closely resemble tennis balls in size and felt texture but differ in pressure. Some padel balls are marked as “Padel” to avoid confusion.
What is the difference between a padel racket and a tennis racket?
The main differences are:
Attribute | Padel Racket | Tennis Racket |
|---|---|---|
Shape | Rounded or teardrop | Oval |
Surface | Solid with perforations (no strings) | Strung with nylon or polyester strings |
Weight | 340g–390g | 260g–350g |
Length | ≤ 455 mm | ≤ 685 mm |
Handle Grip | Short handle | Long handle with extended leverage |
Why doesn’t a padel racket use strings?
Padel rackets use a solid face with perforations to provide better control and redirect speed, which suits the enclosed and rebound-heavy nature of the game.
How does scoring work in padel compared to tennis?
Scoring in both sports follows a similar structure (15, 30, 40, game), but game-deciding conditions differ.
- Padel often uses no-ad scoring, where at deuce (40–40), the next point determines the winner.
- Tennis uses advantage scoring, requiring players to win two consecutive points from deuce for game victory.
How are sets structured in padel?
A match consists of the best of 3 sets, with each set requiring 6 games and a 2-game margin. A 7-point tiebreak is played at 6–6.
How are sets structured in tennis?
Tennis also uses best of 3 or 5 sets (Grand Slams for men). Sets require 6 games with a 2-game margin or tiebreak at 6–6.
What is the average match duration in padel vs tennis?
- Padel matches last approximately 60 minutes.
- Tennis matches average 90 minutes or more, depending on format and rally types.
Padel matches are shorter due to smaller court size and consistent doubles play, whereas tennis singles matches feature longer rallies and more service games.
How does wall usage in gameplay differ?
The function of walls is a key differentiator.
- Padel incorporates glass or mesh walls into gameplay. Players can allow the ball to bounce off walls and return shots afterward, enabling tactical depth.
- Tennis prohibits wall use; once the ball crosses boundaries or contacts any external structure, the point ends or results in a fault.
What tactics rely on wall use in padel?
- Defensive players often let the ball bounce off the back wall to gain position.
- Attackers use angled shots to bounce unpredictably off side walls.
- Lob over net then rebound off glass is a common strategy.
What physical and technical skills are needed in padel?
Padel requires:
- Reflex speed for close-quarter volleys
- Strategic thinking due to frequent wall bounces
- Team coordination since doubles is the only format
- Ball placement control, especially near glass areas
How do padel players develop wall-related techniques?
Skills include:
- Rebound anticipation
- Playing off the back wall under pressure
- Combining lob and smash shots with glass rebounding knowledge
What physical and technical skills are needed in tennis?
Tennis players must develop:
- Explosive footwork, especially for baseline recovery
- Endurance for long rallies and multiple sets
- Technical stroke variety, including serve, forehand, backhand, slice, and topspin
- Tactical variation depending on service game or return game strategy
How do surfaces influence tennis player skills?
- Grass: favors serve-and-volley due to low bounce
- Clay: favors baseline rallies with high topspin
- Hard court: balanced court requiring speed and shot placement
Which is easier to start with: padel or tennis?
Padel offers an easier entry point for beginners.
- Smaller court size increases ball contact frequency
- Required strength is lower due to slower pace and underhand serve
- Wall usage allows longer rally recovery opportunities
Tennis demands more physical conditioning and technical skill from the beginning, including an overhead serve.
What are the main strategic differences between padel and tennis?
Padel emphasizes:
- Ball placement over power
- Positional teamwork
- Use of walls to extend rallies
Tennis emphasizes:
- Dominating with serves and baseline shots
- Solo adaptability in singles
- Surface-based adjustments
Conclusion
Padel and tennis each offer unique gameplay experiences. Padel involves smaller courts, slower balls, wall-integrated tactics, and doubles-only formats, which foster cooperation and strategic rebounds. Tennis emphasizes power, speed, and solo endurance on larger, open courts. Choosing between them comes down to preferred skill sets and physical involvement. Use Padel N Play to locate padel courts nearby and experience the difference firsthand.
